10. Módulo de geometrías: geom¶
Una geometría es un objeto que contiene información geométrica. Estas geometrías tienen un tipo principal: Point, Line, Polygon.. y un subtipo o dimensión: D2, D3, D2M..
Para el Módulo de Scripting hemos creado la librería gvsig.geom que nos ayudará para crear rápidamente las geometrías que necesitemos. Para algunas operaciones más complicadas tendremos que usar la API de gvSIG.
Para establecer estos tipos y subtipos lo haremos utilizando las constantes que se incluyen en la librería.
Constantes que aparecen en la librería gvsig.geom para la creación de geometrías:
#GeometryTypes
AGGREGATE = Geometry.TYPES.AGGREGATE
ARC = Geometry.TYPES.ARC
CIRCLE = Geometry.TYPES.CIRCLE
CURVE = Geometry.TYPES.CURVE
ELLIPSE = Geometry.TYPES.ELLIPSE
ELLIPTICARC = Geometry.TYPES.ELLIPTICARC
GEOMETRY = Geometry.TYPES.GEOMETRY
MULTICURVE = Geometry.TYPES.MULTICURVE
MULTIPOINT = Geometry.TYPES.MULTIPOINT
MULTISOLID = Geometry.TYPES.MULTISOLID
MULTISURFACE = Geometry.TYPES.MULTISURFACE
NULL = Geometry.TYPES.NULL
POINT = Geometry.TYPES.POINT
SOLID = Geometry.TYPES.SOLID
SPLINE = Geometry.TYPES.SPLINE
SURFACE = Geometry.TYPES.SURFACE
# Common named geometry types
POLYGON = Geometry.TYPES.SURFACE
LINE = Geometry.TYPES.CURVE
MULTILINE = Geometry.TYPES.MULTICURVE
MULTIPOLYGON = Geometry.TYPES.MULTISURFACE
# geometrySubTypes
D2 = Geometry.SUBTYPES.GEOM2D
D2M = Geometry.SUBTYPES.GEOM2DM
D3 = Geometry.SUBTYPES.GEOM3D
D3M = Geometry.SUBTYPES.GEOM3DM
UNKNOWN = Geometry.SUBTYPES.UNKNOWN
# Dimensions
DIMENSIONS = Geometry.DIMENSIONS
Ejemplo testeando la librería de geom:
import gvsig
reload(gvsig)
from gvsig import *
from gvsig import geom
def main(*args):
# Create Polygon
print "\nCreate Polygon"
x = geom.createPolygon()
pol_1 = geom.createPolygon(vertexes=[geom.createPoint(geom.D2, 4,5),geom.createPoint(geom.D2,3,3),geom.createPoint(geom.D2,3,2),geom.createPoint(geom.D2,4,5)])
print "pol_1: ", pol_1.convertToWKT()
pol_2 = geom.createPolygon(vertexes=[geom.createPoint(geom.D2,4,5),geom.createPoint(geom.D2,3,3),geom.createPoint(geom.D2,3,2),geom.createPoint(geom.D2,4,5)])
print "pol_2: ", pol_2.convertToWKT()
pol_3 = geom.createPolygon(vertexes=[geom.createPoint(geom.D2,4,5),geom.createPoint(geom.D2,3,3),geom.createPoint(geom.D2,3,2),geom.createPoint(geom.D2,4,5)])
print "pol_3: ", pol_3.convertToWKT()
pol_4 = geom.createPolygon(geom.D2,[(0,0),(10,10),[3,3],[3,6],[0,0]])
print "pol_4: ", pol_4.convertToWKT()
# Create MultiPolygon
print "\nCreate MultiPolygon"
multipolygon1 = geom.createMultiPolygon()
multipolygon1.addSurface(pol_1)
multipolygon1.addSurface(pol_2)
multipolygon1.addSurface(pol_3)
print "multipolygon1: ", multipolygon1.convertToWKT()
multipolygon2 = geom.createMultiPolygon(polygons=[pol_1, pol_2, pol_3])
print "multipolygon2: ", multipolygon2.convertToWKT()
p2 = geom.createPoint(geom.D2,1,2)
print "p2:", p2
line2 = geom.createLine(geom.D2, [[10,19],p2,[5,2]])
print line2
print line2.convertToWKT()
y = geom.createPoint(geom.D3M,10,1,5,8)
z = geom.createPoint(geom.D3,10, 1, 5)
print "point y: ", y,type(y)
print "point z", z, type(z)
print "preparing 3d"
x = geom.createLine(geom.D3M,[(10,10,100,8),(1,95,2,8)])
print x.convertToWKT()
# Create point
print "\nCreate Point"
point1 = geom.createPoint(geom.D2,10, 10)
point2 = geom.createGeometry(geom.POINT)
point2.setX(15)
point2.setY(15)
print "Point1: ", point1
print "Point2: ", point2
point1 = geom.createPoint(geom.D2,10, 10)
# Create line
print "\nCreate Line"
line1 = geom.createGeometry(geom.LINE)
line1.addVertex(geom.createPoint(geom.D2,0,0))
line1.addVertex(geom.createPoint(geom.D2,10,10))
print "Line1: ", line1.convertToWKT()
p2 = geom.createPoint(geom.D2,1,2)
print " === LINE == "
line2 = geom.createLine(geom.D2, [[10,19], point1 ,p2,[5,2]])
print "Line2 object: ", line2
print "Line2: ", line2.convertToWKT()
print "1", line2.getVertex(0)
print "2", line2.getVertex(1)
print "3", line2.getVertex(2)
print "4", line2.getVertex(3)
# Create polygon
print "\nCreate Polygon"
g = geom.createGeometry(geom.POLYGON)
g.addVertex(geom.createPoint(geom.D2,0,0))
g.addVertex(geom.createPoint(geom.D2,10,10))
g.addVertex(geom.createPoint(geom.D2,10,0))
g.addVertex(geom.createPoint(geom.D2,0, 0))
print "JTS of the Polygon 1: ", g.convertToWKT()
g.setVertex(2, geom.createPoint(geom.D2, 15, 15))
print "JTS of the Polygon 1 modified: ", g.convertToWKT()
poli_1 = geom.createPolygon(geom.D2, [[0,0],[1,1],[2,3],[3,6],[0,0]])
print "Poli_1", poli_1.convertToWKT()
poli_2 = geom.createPolygon(geom.D3, [[0,1,2],[1,1,5],geom.createPoint(geom.D3,2,1,5),[0,1,2]])
print "Poli_2", poli_2
# Create gvSIG geometry from a WKT or WKB
print "\nCreate gvSIG geometry from WKT or WKB"
wkt = "POLYGON ((0 0, 150 150, 100 0, 0 0))"
x = geom.createGeometryFromWKT(wkt)
print "Polygon from WKT: ", x
print "Type polygon: ", type(x)
# Create 3D geometry
print "\nCreate 3D Geometry"
p3d = geom.createGeometry(geom.POINT, geom.D3)
p3d.setX(10)
p3d.setY(10)
p3d.setZ(100)
print "Point 3D: ", p3d, type(p3d)
p1_3d = geom.createPoint(geom.D3,1,3,3)
print "Point 3D P1: ", p1_3d
# Create Multipoint
print "\nCreate Multipoint: "
multipoint1 = geom.createMultiPoint(points=[geom.createPoint(geom.D2, 10,10), geom.createPoint(geom.D2,5,2), geom.createPoint(geom.D2,8,3)])
print "multipoint1: ", multipoint1.convertToWKT()
multipoint1.addPrimitive(geom.createPoint(geom.D2,3, 2))
print "multipoint1 modified: ", multipoint1.convertToWKT()
multipoint2 = geom.createMultiPoint()
print "multipoint2: ", multipoint2.convertToWKT()
multipoint3 = geom.createMultiPoint(geom.D3,[[19,10,8],[3,5,7],[35,5,5]])
print "multipoint3: ", multipoint3.convertToWKT()
# Create Polygon
print "\nCreate Polygon"
x = geom.createPolygon()
pol_1 = geom.createPolygon(vertexes=[geom.createPoint(geom.D2,4,5),geom.createPoint(geom.D2,3,3),geom.createPoint(geom.D2,3,2),geom.createPoint(geom.D2,4,5)])
print "pol_1: ", pol_1.convertToWKT()
pol_2 = geom.createPolygon(vertexes=[geom.createPoint(geom.D2,4,5),geom.createPoint(geom.D2,3,3),geom.createPoint(geom.D2,3,2),geom.createPoint(geom.D2,4,5)])
print "pol_2: ", pol_2.convertToWKT()
pol_3 = geom.createPolygon(vertexes=[geom.createPoint(geom.D2,4,5),geom.createPoint(geom.D2,3,3),geom.createPoint(geom.D2,3,2),geom.createPoint(geom.D2,4,5)])
print "pol_3: ", pol_3.convertToWKT()
pol_4 = geom.createPolygon(geom.D2,[(0,0),(10,10),[3,3],[3,6],[0,0]])
print "pol_4: ", pol_4.convertToWKT()
# Create MultiPolygon
print "\nCreate MultiPolygon"
multipolygon1 = geom.createMultiPolygon()
multipolygon1.addSurface(pol_1)
multipolygon1.addSurface(pol_2)
multipolygon1.addSurface(pol_3)
print "multipolygon1: ", multipolygon1.convertToWKT()
multipolygon2 = geom.createMultiPolygon(polygons=[pol_1, pol_2, pol_3])
print "multipolygon2: ", multipolygon2.convertToWKT()
multipolygon3 = geom.createMultiPolygon(geom.D2,[[[0,0],[1,1],[2,2],[0,0]],[[2,5],[3,5],[1,2],[2,5]],pol_4])
print "multipolygon3: ", multipolygon3.convertToWKT()
# CreateLine
print "\nCreate Line"
line1 = geom.createLine()
line1.addVertex(geom.createPoint2D(1,1))
line1.addVertex(geom.createPoint2D(3,3))
print "line1: ", line1.convertToWKT()
line2 = geom.createLine(vertexes=[geom.createPoint2D(0,0), geom.createPoint2D(10,10)])
print "line2: ", line2.convertToWKT()
line3 = geom.createLine(geom.D2,[[0,1],[1,5],[5,3]])
print "line3: ", line3.convertToWKT()
# Create MultiLine
print "\nCreate MultiLine"
multiline1 = geom.createMultiLine()
multiline1.addCurve(line1)
multiline1.addCurve(line2)
print "multiline1: ", multiline1.convertToWKT()
multiline2 = geom.createMultiLine(lines=[line1, line2], subtype=geom.D2)
print "multiline2: ", multiline2.convertToWKT()
# Create Envelope
envelope = geom.createEnvelope(pointMin=geom.createPoint2D(10,0),pointMax=geom.createPoint2D(10,20))
print "envelope: ", envelope
env1 = geom.createEnvelope(point1,[38,29])
print "env1: ", env1,type(env1)
# Create from WKT
print "\nCreate geometr from WKT"
wkt = geom.createGeometryFromWKT("MULTIPOLYGON (((4 5, 3 3, 3 2, 4 5)), ((4 5, 3 3, 3 2, 4 5)), ((4 5, 3 3, 3 2, 4 5)))")
print "wkt: ", wkt.convertToWKT()
# Create 2D
pg = geom.createPoint2D(19,5)
print pg
lg = geom.createLine2D()
print lg
mg = geom.createPolygon2D()
print mg
mg2 = geom.createPolygon2D([[1,5],[4,5],[1,3],[25,2],pg,[1,5]])
print mg2.convertToWKT()
x = geom.createPoint2D(1)
print x
10.1. Punto¶
Creando puntos:
from gvsig.geom import *
def main(*args):
print "\nCreate Point"
point1 = createPoint(D3, 10, 10, 5)
point2 = createPoint(D2, 15, 7)
point3 = createGeometry(POINT)
point3.setX(15)
point3.setY(15)
point4 = createPoint(D3M, 5, 18, 3, 2)
print "Point1: ", point1
print "Point2: ", point2
print "Point3: ", point3
print "Point4: ", point4
Consola:
Create Point
Point1: POINT Z (10.0 10.0 5.0)
Point2: POINT (15.0 7.0)
Point3: POINT (15.0 15.0)
Point4: POINT ZM (5.0 18.0 3.0 2.0)
Creando punto con 3 dimensiones:
from gvsig.geom import *
def main(*args):
#Create 3D Geometry
p3d = createGeometry(POINT, D3)
p3d.setX(10)
p3d.setY(10)
p3d.setZ(100)
print p3d.convertToWKT()
Consola:
POINT Z (10 10 100)
10.2. Línea¶
Creando líneas:
from gvsig.geom import *
def main(*args):
line1 = createGeometry(LINE)
line1.addVertex(createPoint(D2,0,0))
line1.addVertex(createPoint(D2,10,10))
print "Line1: ", line1.convertToWKT()
Consola:
Line1: LINESTRING (0 0, 10 10)
Accediendo a los vértices de la línea:
from gvsig.geom import *
def main(*args):
line1 = createGeometry(LINE)
line1.addVertex(createPoint(D2,0,0))
line1.addVertex(createPoint(D2,10,10))
print "Line1: ", line1.convertToWKT()
p1 = createPoint(D2, 3, 01)
p2 = createPoint(D2, 1, 2)
# List of vertex or coordinates
vertx = [[10,19], p1 ,p2,[5,2]]
line2 = createLine(D2, vertx)
print "\nLine2 object: ", line2
print "Line2: ", line2.convertToWKT()
print "1", line2.getVertex(0)
print "2", line2.getVertex(1)
print "3", line2.getVertex(2)
print "4", line2.getVertex(3)
Consola:
Line1: LINESTRING (0 0, 10 10)
Line2 object: Line:2D
Line2: LINESTRING (10 19, 3 1, 1 2, 5 2)
1 POINT (10.0 19.0)
2 POINT (3.0 1.0)
3 POINT (1.0 2.0)
4 POINT (5.0 2.0)
10.3. Polígono¶
Creando polígonos:
from gvsig.geom import *
def main(*args):
g = createGeometry(POLYGON, D2)
g.addVertex(createPoint(D2,0,0))
g.addVertex(createPoint(D2,10,10))
g.addVertex(createPoint(D2,10,0))
g.addVertex(createPoint(D2,0, 0))
print "WKT Polygon: ", g.convertToWKT()
poli_1 = createPolygon(D2, [[0,0],[1,1],[2,3],[3,6],[0,0]])
print "Poli_1", poli_1.convertToWKT()
poli_2 = createPolygon(D3, [[0,1,2],[1,1,5],createPoint(D3,2,1,5),[0,1,2]])
print "Poli_2", poli_2.convertToWKT()
Consola:
WKT Polygon: POLYGON ((0 0, 10 10, 10 0, 0 0))
Poli_1 POLYGON ((0 0, 1 1, 2 3, 3 6, 0 0))
Poli_2 POLYGON Z ((0 1 2, 1 1 5, 2 1 5, 0 1 2))
10.4. Multipunto¶
Creando multipunto:
from gvsig.geom import *
def main(*args):
# Create Multipoint
multipoint1 = createMultiPoint(D2, [createPoint(D2, 10,10), createPoint(D2,5,2), createPoint(D2,8,3)])
print "multipoint1: ", multipoint1.convertToWKT()
multipoint2 = createMultiPoint()
print "multipoint2: ", multipoint2.convertToWKT()
multipoint3 = createMultiPoint(D3,[[19,10,8],[3,5,7],[35,5,5]])
print "multipoint3: ", multipoint3.convertToWKT()
Consola:
multipoint1: MULTIPOINT (10 10, 5 2, 8 3)
multipoint2: MULTIPOINT EMPTY
multipoint3: MULTIPOINT Z (19 10 8, 3 5 7, 35 5 5)
Añadiendo punto a una geometría de tipo multipunto:
from gvsig.geom import *
def main(*args):
# Create Multipoint
multipoint1 = createMultiPoint(D2, [createPoint(D2, 10,10), createPoint(D2,5,2), createPoint(D2,8,3)])
print "multipoint1: ", multipoint1.convertToWKT()
multipoint1.addPrimitive(createPoint(D2,3, 2))
print "multipoint1 modified: ", multipoint1.convertToWKT()
Consola:
multipoint1: MULTIPOINT (10 10, 5 2, 8 3)
multipoint1 modified: MULTIPOINT (10 10, 5 2, 8 3, 3 2)
10.5. Multilínea¶
Creando multilíneas:
from gvsig.geom import *
def main(*args):
# CreateLine
print "\nCreate Line"
line1 = createLine()
line1.addVertex(createPoint2D(1,1))
line1.addVertex(createPoint2D(3,3))
line2 = createLine(vertexes=[createPoint2D(0,0), createPoint2D(10,10)])
line3 = createLine(D2,[[0,1],[1,5],[5,3]])
# Create MultiLine
multiline1 = createMultiLine()
multiline1.addCurve(line1)
multiline1.addCurve(line2)
print "multiline1: ", multiline1.convertToWKT()
multiline2 = createMultiLine(D2, lines=[line1, line2])
print "multiline2: ", multiline2.convertToWKT()
multiline3 = createGeometry(MULTICURVE, D2)
multiline3.addCurve(line1)
multiline3.addCurve(line3)
print "multiline3: ", multiline3.convertToWKT()
Consola:
Create Line
multiline1: MULTILINESTRING ((1 1, 3 3), (0 0, 10 10))
multiline2: MULTILINESTRING ((1 1, 3 3), (0 0, 10 10))
multiline3: MULTILINESTRING ((1 1, 3 3), (0 1, 1 5, 5 3))
10.6. Multipolígono¶
Creando multipolígonos:
from gvsig.geom import *
def main(*args):
# Create Polygon
x = createPolygon()
pol_1 = createPolygon(vertexes=[createPoint(D2,4,5),createPoint(D2,3,3),createPoint(D2,3,2),createPoint(D2,4,5)])
pol_2 = createPolygon(vertexes=[createPoint(D2,4,5),createPoint(D2,3,3),createPoint(D2,3,2),createPoint(D2,4,5)])
pol_3 = createPolygon(vertexes=[createPoint(D2,4,5),createPoint(D2,3,3),createPoint(D2,3,2),createPoint(D2,4,5)])
pol_4 = createPolygon(D2,[(0,0),(10,10),[3,3],[3,6],[0,0]])
# Create MultiPolygon
multipolygon1 = createMultiPolygon()
multipolygon1.addSurface(pol_1)
multipolygon1.addSurface(pol_2)
multipolygon1.addSurface(pol_3)
print "multipolygon1: ", multipolygon1.convertToWKT()
multipolygon2 = createMultiPolygon(polygons=[pol_1, pol_2, pol_3]) #2D as default
print "multipolygon2: ", multipolygon2.convertToWKT()
multipolygon3 = createMultiPolygon(D2, [[[0,0],[1,1],[2,2],[0,0]],
[[2,5],[3,5],[1,2],[2,5]],
pol_4])
print "multipolygon3: ", multipolygon3.convertToWKT()
multipolygon4 = createMultiPolygon()
print "multipolygon4: ", multipolygon4.convertToWKT()
Consola:
multipolygon1: MULTIPOLYGON (((4 5, 3 3, 3 2, 4 5)), ((4 5, 3 3, 3 2, 4 5)), ((4 5, 3 3, 3 2, 4 5)))
multipolygon2: MULTIPOLYGON (((4 5, 3 3, 3 2, 4 5)), ((4 5, 3 3, 3 2, 4 5)), ((4 5, 3 3, 3 2, 4 5)))
multipolygon3: MULTIPOLYGON (((0 0, 1 1, 2 2, 0 0)), ((2 5, 3 5, 1 2, 2 5)), ((0 0, 10 10, 3 3, 3 6, 0 0)))
multipolygon4: MULTIPOLYGON EMPTY
10.7. Envelope¶
Crear Envelope del tipo Envelope2D
from gvsig.geom import *
def main(*args):
# Create Envelope
envelope = createEnvelope(pointMin=createPoint2D(10,0),pointMax=createPoint2D(10,20))
print "envelope: ", envelope
point1 = createPoint(D2, 0, 0)
env1 = createEnvelope(point1,[38,29])
print "env1: ", env1
print "env1 type: ", type(env1)
Consola:
envelope: POLYGON ((10.0 0.0, 10.0 20.0, 10.0 20.0, 10.0 0.0, 10.0 0.0))
env1: POLYGON ((0.0 0.0, 0.0 29.0, 38.0 29.0, 38.0 0.0, 0.0 0.0))
env1 type: <type 'org.gvsig.fmap.geom.jts.primitive.Envelope2D'>
10.8. WKT¶
Crear geometría desde un WKT:
from gvsig.geom import *
def main(*args):
# Create from WKT
wkt = createGeometryFromWKT("MULTIPOLYGON (((4 5, 3 3, 3 2, 4 5)), ((4 5, 3 3, 3 2, 4 5)), ((4 5, 3 3, 3 2, 4 5)))")
print "wkt: ", wkt.convertToWKT()
Consola:
wkt: MULTIPOLYGON (((4 5, 3 3, 3 2, 4 5)), ((4 5, 3 3, 3 2, 4 5)), ((4 5, 3 3, 3 2, 4 5)))
10.9. Operaciones espaciales¶
Puedes consultar todas las operaciones espaciales en el interfaz de geometrías Geometry
Distancia entre puntos:
from gvsig.geom import *
def main(*args):
# Creamos punto2
point1 = createPoint(D2, 0, 0)
point2 = createPoint(D2, 10, 10)
print "Distance 2D: ", point1.distance(point2)
point3 = createPoint(D3, 0, 0, 100)
point4 = createPoint(D3, 10, 10, 0)
print "Distance 2D: ", point3.distance(point4)
Consola:
Distance 2D: 14.1421356237
Distance 2D: 14.1421356237
Moviendo un punto:
from gvsig.geom import *
def main(*args):
# Creamos punto2
point1 = createPoint(D2, 10, 10)
print "Point 1: ", point1.convertToWKT()
#Move point
point1.move(5, -3)
print "Moved point by 5, -3: ", point1.convertToWKT()
Consola:
Point 1: POINT (10 10)
Moved point by 5, -3: POINT (15 7)
Operaciones entre polígonos y líneas:
from gvsig.geom import *
def main(*args):
# Creamos punto2
point1 = createPoint(D2, 0, 0)
buffer1 = point1.buffer(10)
line1 = createLine(D2, [[-5, -5],[10, 10]])
print "Intersects?: ", buffer1.intersects(line1)
print "Intersection: ", buffer1.intersection(line1).convertToWKT()
Consola:
Intersects?: True
Intersection: LINESTRING (-5 -5, 7.071067811865473 7.071067811865473)
Operaciones espaciales entre polígonos:
from gvsig.geom import *
def main(*args):
# Creamos punto2
point1 = createPoint(D2, 0, 0)
# Aplicamos un area de influencia buffer(m)
buffer1 = point1.buffer(10)
print "Buffer1 Area: ", buffer1.area()
# Creamos punto 2
point2 = createPoint(D2, 8, 0)
buffer2 = point2.buffer(5)
print "Buffer2 Area: ", buffer2.area()
# Union
buffer12_union = buffer1.union(buffer2)
print "Buffer12 Union Area: ", buffer12_union.area()
# Differencia
buffer12_diff = buffer1.difference(buffer2)
print "Buffer12 Difference Area: ", buffer12_diff.area()
Consola:
Buffer1 Area: 312.144515226
Buffer2 Area: 78.0361288065
Buffer12 Union Area: 335.886462528
Buffer12 Difference Area: 257.850333721
Creando un polígono, aplicarle un área de influencia, añadirle un anillo interno y agregarlo en una capa nueva:
from gvsig import *
from gvsig.geom import *
def main(*args):
pol_1 = createPolygon(D2M, [(0,0),(300,0),(300,300),(0,300),(0,0)])
# Add interior ring
pol_1x = createPolygon(D2M, pol_1).buffer(200)
pol_1x.addInteriorRing(pol_1)
schema = createSchema()
schema.append("ID", "STRING", 5)
schema.append("GEOMETRY", "GEOMETRY")
schema.get('GEOMETRY').setGeometryType(POLYGON, D2M)
shape = createShape(schema ,CRS='EPSG:25830')
shape.edit()
shape.append(ID=1, GEOMETRY=pol_1x)
shape.commit()
currentView().addLayer(shape)

Ejemplo para extraer todos los vértices de una capa de polígonos en forma de multipuntos:
# encoding: utf-8
from gvsig import *
from gvsig import geom
def main(*args):
""" Extraer vertices de poligonos como multipuntos """
layer = currentLayer()
features = layer.features()
sch = createFeatureType()
sch.append("GEOMETRY", "GEOMETRY")
sch.get("GEOMETRY").setGeometryType(geom.MULTIPOINT, geom.D2)
shp = createShape(sch)
for feature in features:
gf = feature.geometry()
shp.append(GEOMETRY=gf.toPoints())
shp.commit()
currentView().addLayer(shp)
Resultado:
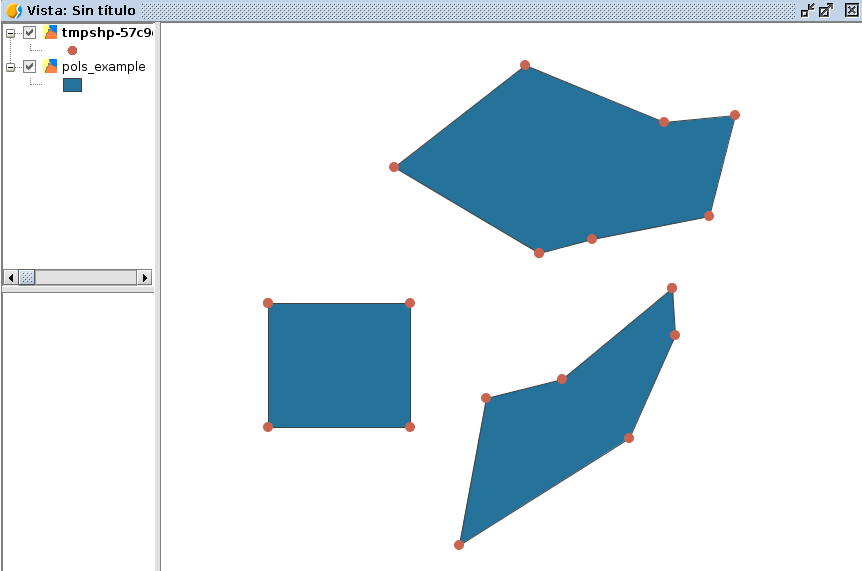
Con una pequeña modificación, podemos hacer que añada un punto por cada vértice, recorriendo las geometrías de multipunto y extrayendo uno a uno sus puntos:
# encoding: utf-8
from gvsig import *
from gvsig import geom
def main(*args):
""" Extraer vertices de poligonos como multipuntos """
layer = currentLayer()
features = layer.features()
sch = createFeatureType()
sch.append("GEOMETRY", "GEOMETRY")
sch.get("GEOMETRY").setGeometryType(geom.POINT, geom.D2)
shp = createShape(sch)
for feature in features:
gf = feature.geometry()
for p in gf:
shp.append(GEOMETRY=p)
shp.commit()
currentView().addLayer(shp)
Otra forma de recorrer los vertices podría ser haciendo uso del método getVertex y getNumVertices:
# encoding: utf-8
from gvsig import *
from gvsig import geom
def main(*args):
""" Extraer vertices de poligonos como multipuntos """
layer = currentLayer()
features = layer.features()
for feature in features:
gf = feature.geometry()
numvertices = gf.getNumVertices()
print "Vertices: ", numvertices
for i in range(0, numvertices):
print gf.getVertex(i) #geometria de tipo punto
Dando por consola una salida similar a:
Vertices: 7
POINT (274.17769116287 194.9280163662371)
POINT (275.81171697787 166.3325646037371)
POINT (248.03327812287003 105.05659654123708)
POINT (145.90666468537003 40.5125768487371)
POINT (162.24692283537004 128.74997085873707)
POINT (207.99964565537007 140.1881515637371)
POINT (274.17769116287 194.9280163662371)
...
10.10. Transformación entre proyecciones¶
En el siguiente ejemplo vemos como transformar una geometría entre dos proyecciones:
# encoding: utf-8
from gvsig import *
from gvsig.geom import *
def main(*args):
""" Convertir geometria entre proyecciones """
crs1 = getCRS('EPSG:4326')
crs2 = getCRS('EPSG:32630')
#Get IProjection
#view1 = currentProject().getViews()[0].getProjection()
#view2 = currentProject().getViews()[1].getProjection()
#Get ICoordTrans
ICoordTrans1 = crs1.getCT(crs2)
point = createPoint2D(-0.375,39.466) #Valencia
print "point: ", point
point.reProject(ICoordTrans1)
print "reprojected: ", point



