Manual de usuario gvSIG 1.9
With this type of filter, graphical transformations like smoothing, edge detection, sharpening etc. are applied to the image.
The following filter types can be applied:
MEDIAN FILTER
The median filter applies a kernel of a certain size, which is determined by the user through the sliding bar labeled Window side.
The median filter is normally used to smoothen and to reduce noise in an image, by moving a kernel of N x N number of pixels over the image and evaluating each central pixel, replacing its value with the median of its neighboring pixels. Compared to the Mean filter, the advantage of the Median filter is that the final pixel value is a value that actually occurs in the image and not an average.
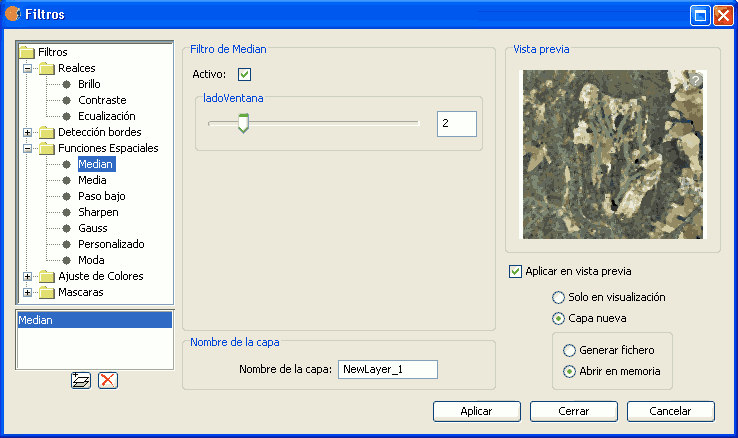
Median filter
MEAN FILTER
The mean filter applies a kernel of a certain size, which is determined by the user through the sliding bar labeled Window side.
The filter replaces the value of the central pixel with the mean value of the surrounding pixels. Each value of the kernel would be one and the divider would be the total number of elements in the kernel (i.e. a kernel of 3 x 3 would replace the value of the central pixel by the average value of the nine pixels covered by the kernel).
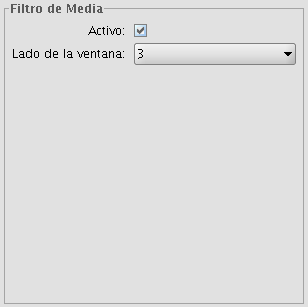
Mean filter
LOW PASS FILTER (smoothing filter)
The low pass filter applies a kernel of a certain size, which is determined by the user through the sliding bar labeled Window side.
Using a low pass filter tends to retain the low frequency information within an image while reducing the high frequency information.
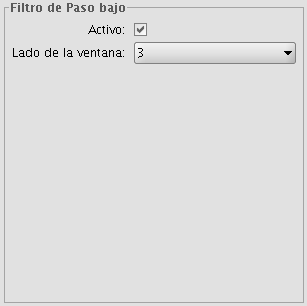
Low pass filter
SHARPENING FILTER
By moving the slider to change the sharpness (values from 1-100), the contrast of an image can be changed. The results can be evaluated in the preview window. With a higher contrast, details in the image can be accentuated but the noise will also increase.
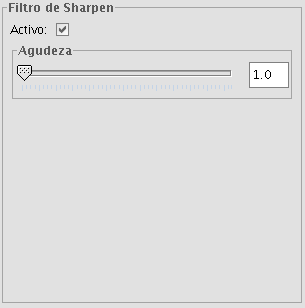
Sharpening filter
GAUSS FILTER
The Gauss filter applies a kernel of a certain size, which is determined by the user through the sliding bar labeled Window side.
The maximum value appears in the central pixel and gradually decreases for pixels that are further away from the central pixel.
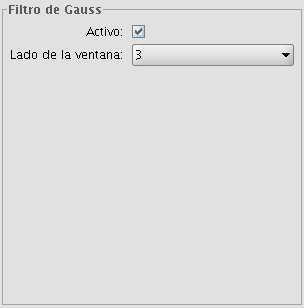
Gauss filter
CUSTOM FILTER
This is a kernel of 5 x 5 or 3 x 3, for which the values can be introduced by the user. After multiplying the pixel values with the kernel values, the result will be divided by the number specified in the Divisor textbox.
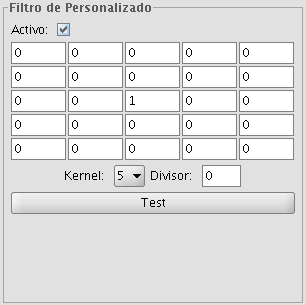
Custom filter
MODE FILTER
The mode filter applies a kernel of a certain size, which is determined by the user through the sliding bar labeled Window side.
This filter takes the value that occurs most in the surrounding pixels and assigns it to the central pixel.
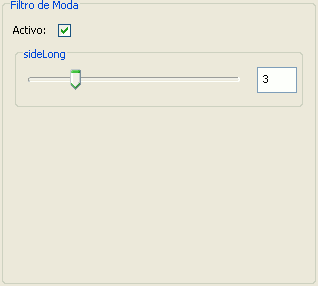
Moda filter









