gvSIG-Desktop 1.11. User manual
Editing properties
Introduction
When a layer editing session has been started, if you right click on its name in the ToC, a contextual menu appears in which, among other things, you can access the “Edition properties” to configure them.
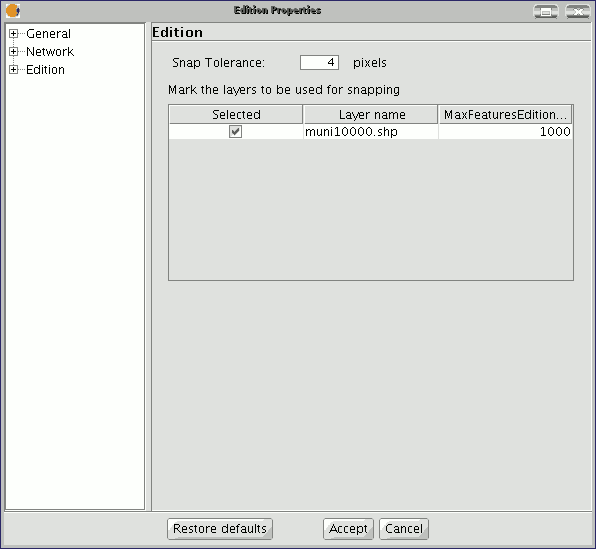
Snapping
You can configure the “Snap tolerance” in the first editing page. “Snap” or “Snapping” is the process of moving an element until it coincides exactly with the coordinates of another element. If the “Snap tolerance” is 4 pixels, two elements which are the same distance or closer than 4 pixels will be joined in a common coordinate.
You can do element snapping between layers by enabling the corresponding check boxes in the “Selected” column.
You can modify the values of the "Maximum features edition cache" column to accelerate the snappings and handlers being edited. This is the maximum number of geometries you wish to work with in the cache.
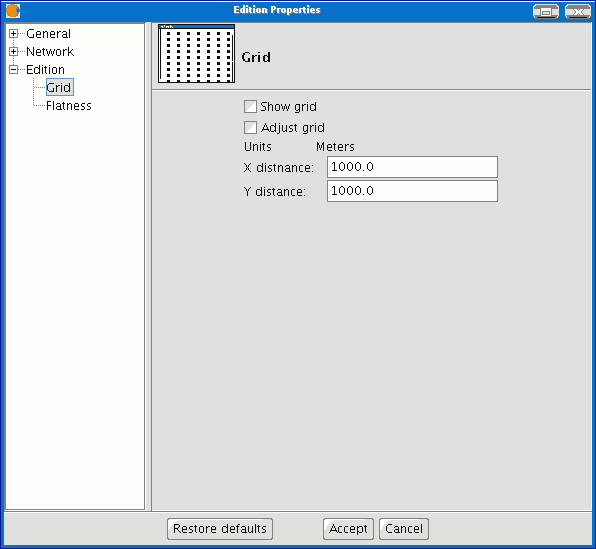
Configuring the grid
If you select "Grid" in the tree on the left, this will allow you to configure the grid's properties.
The grid is a point pattern which extends over the whole of the graphic area. It is useful in that it allows you to line up objects and calculate the distance between them.
You can enable the “Show grid” and “Adjust to grid” check boxes and edit the distance between the grid points.
When the grid is shown, the graphic area will look like this.

Flatness
You can configure “Flatness” by selecting the corresponding option in the tree on the left.
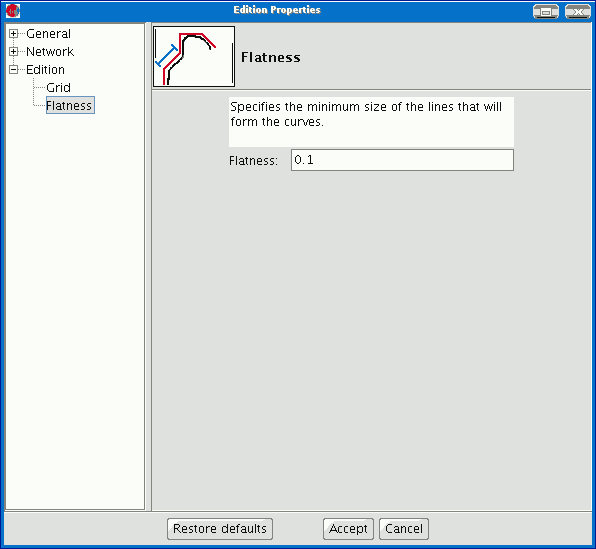
In gvSIG, a circle or any curved geometry is made up of straight sections. The flatness number you specify will define the maximum size of these sections.









