gvSIG-Desktop 1.11. User manual
A point can be referenced in two ways:
- Console mode. The point coordinates are input numerically.
- Graphic mode. The point is indicated by using any of the pointer devices (normally a mouse).
The coordinates can also be:
- Absolute: They define a point based on the coordinate source (0,0).
- Relative: They define a point based on the last defined point.
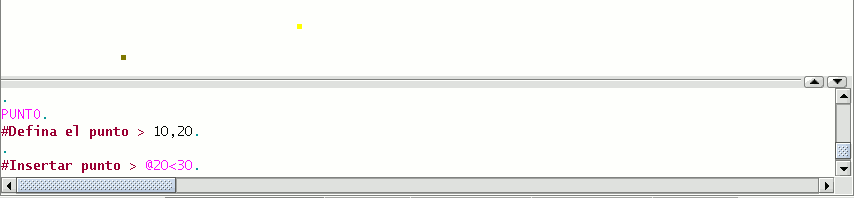
Inputting Cartesian coordinates.
Input the X and Y values separated by a comma (X,Y). The X value is the positive or negative distance, in units along the horizontal axis, the Y value is the distance in units along the vertical axis.
The values used to designate the points can be whole, decimal, positive or negative.
The absolute coordinate values are based on the source (0,0), which is the place the X and Y axes intersect. For example, the point 25,7 designates a point located 25 units away from the source on the X axis and 7 units away on the Y axis.
The relative values of the coordinates are based on the last input point. Use the relative coordinates when you know the coordinates of a point based on the previous point.
To designate a relative point, place the (@) symbol in front of the coordinates.
For example, the @1,2 coordinates determines a point 1 unit away on the X axis and 2 units away on the Y axis from the previously designated point.
Inserting polar coordinates
To input polar coordinates, indicate a distance and an angle separated by the < symbol. For example, to designate a point 5 units away from the previous one with a 45 degree angle, write @5<45. The angles increase anti-clockwise and decrease clockwise. To move anti-clockwise, indicate a negative angle. For example, the 1<315 position is the same as the 1<-45 position.